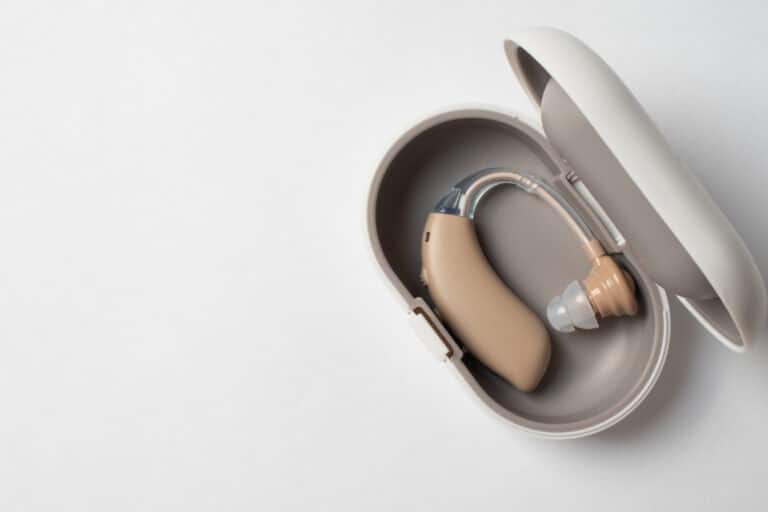
Hearing aids have traditionally been prescribed and fitted by audiologists or hearing healthcare professionals. However, over-the-counter hearing aids are becoming increasingly popular as an alternative to traditional methods. OTC devices offer convenience and affordability, but there’s a lot to consider before making this type of purchase.
OTC hearing aids are relatively new to the market and are classified as Class I Over-the-counter hearing aids. These devices are designed to be easy to use and affordable, with limited features and settings that the user can adjust. They are ideal for patients with mild to moderate hearing loss.
How Do Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids Work?
OTC hearing aids work in the same way as traditional prescription models. They are designed to amplify sound and make it easier for a person to hear clearly. OTC devices come with pre-programmed settings that can be adjusted to fit the user’s needs and preferences.
Over-the-counter hearing aids are relatively small, lightweight and comfortable. They feature a microphone that picks up sound waves, amplifies them and sends them to the speaker, which can be an earbud or a behind-the-ear device. OTC devices are powered by batteries and may have limited capabilities.
In order to make an informed decision, it is important to weigh the pros and cons before investing in them. Here are 10 pros and cons of OTC hearing aids that you should be aware of when considering buying one.
PROS of OTC Hearing Aids
#1 – Convenience
Since OTC hearing aids are available online or at a retail store, they offer a convenient option for those who are unable to make an appointment with an audiologist. They also require minimal paperwork, making them a great choice if you’re looking for a quick and easy solution.
#2 – Cost
Generally, Over-the-counter hearing aids are more affordable than their custom-made counterparts. They are often less expensive due to the simplified design and fewer features, making them an attractive option for those on a budget.
#3 – Discreetness
Over-the-counter hearing aids tend to be smaller in size compared to prescription devices, which makes them more discreet. They can be worn inside or outside of the ear, allowing you to blend in with your surroundings.
#4 – Accessibility:
Over-the-counter hearing aids enhance accessibility, allowing users to easily purchase and replace them without the need for repeated appointments. This is especially beneficial for individuals in remote areas or those with busy schedules.
#5 – Trial and Error:
OTC devices offer a trial-and-error advantage. Users can experiment with different models to find the one that best suits their preferences without the commitment typically associated with prescription hearing aids.
#6 – Technological Advancements:
As the demand for OTC hearing aids grows, manufacturers are investing in research and development. This could lead to improved technology and expanded features in future OTC models, providing users with increasingly advanced options.
CONS of OTC Hearing Aids

#1 – Fit and Comfort
Without the proper fit and adjustment, over-the-counter device users may experience discomfort or pain due to incorrect size. With prescription devices, you can opt for custom-made shells that fits your ear properly, ensuring a comfortable fit.
#2 – Limited Adjustments and Settings
Due to OTC hearing aids having a limited number of adjustments and settings, they may not be suitable for individuals with more severe forms of hearing loss. They are generally not programmable, leaving the user with little to no control over how their device works.
#3 – Quality
If you’re looking for exceptional sound quality and modern technology, over-the-counter hearing aids may not be your best option. They tend to have lower sound quality and fewer features than prescription models, which can limit the user’s ability to hear clearly.
#4 – Lack of Personalization:
Prescription hearing aids often come with personalized programming to address specific hearing needs. OTC devices, with their limited adjustments, might not provide the same level of customization, potentially leading to suboptimal performance for some users.
#5 – Professional Guidance:
Opting for over-the-counter hearing aids means foregoing the expertise of audiologists who can assess individual needs comprehensively. Professionals play a crucial role in identifying underlying health issues related to hearing loss that may require medical attention.
Consult the Best Audiologists in Westchester County

While over-the-counter devices offer significant benefits, its best to understand your case and get the best hearing aid for you. In addition, they may not provide the same level of support and care as those provided by a licensed hearing healthcare professional.
Listen Hear Diagnostics is the leading hearing specialist and audiologist in Westchester, NY, providing the best hearing loss treatment and customized hearing aids for patients. We offer some of the most trusted and modern brands in the hearing aids industry and provide our patients with options depending on their budget. We also provide comprehensive hearing assessment, hearing aid evaluation and repair, and continuing support and care for clients with hearing loss.
Contact us to schedule your hearing aid fitting today! We are located at 161 S Central Park Avenue, Hartsdale, NY. Our office accepts all credit cards and are in-network with a lot of health insurance providers. We will help you manage the cost and provide the best hearing solution for you.






