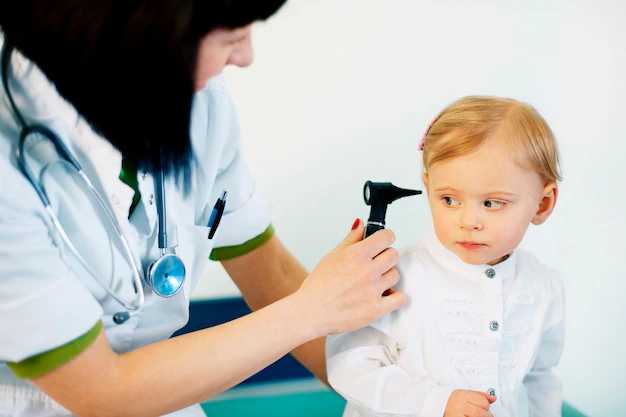
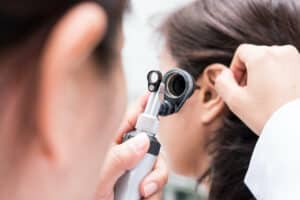
Hearing plays a fundamental role in a child’s development, communication, and learning. However, hearing disorders and conditions can affect children at different stages, potentially hindering their progress and well-being. Pediatric audiology, a specialized branch of audiology, focuses on understanding and addressing the unique auditory needs of children.
This blog takes you on a journey through pediatric audiology, understanding its core principles, common hearing challenges faced by children, and the importance of early detection. We’ll explore the evaluation process used by pediatric audiologists in Westchester to assess a child’s hearing abilities. Additionally, we’ll address the emotional impact on both children and their families, offering valuable resources for support.
Join us on this enlightening exploration of pediatric audiology and its vital role in ensuring a brighter future for our children. Let’s create a world where every child’s voice is heard.
Understanding Pediatric Audiology
Pediatric audiology is a specialized field that focuses on assessing and managing hearing-related issues in children. Unlike adults, children’s hearing abilities are in various stages of development, making their auditory needs unique and requiring tailored approaches to diagnosis and intervention.
One of the primary objectives of pediatric audiology is to detect hearing problems as early as possible. Early detection is critical because the auditory system develops rapidly during the early years of life, and any delays or issues can significantly impact a child’s language acquisition and overall communication skills. Identifying hearing impairments early allows for timely intervention, maximizing the potential for improved outcomes.
Role of a Pediatric Audiologist
Pediatric audiologists possess expertise in working with children of all ages, from newborns to adolescents. They employ specialized techniques and tools to assess the hearing abilities of young patients, often relying on behavioral observations and objective measures. These assessments may include play audiometry, visual reinforcement audiometry, and otoacoustic emissions tests, among others.
Understanding the challenges faced when evaluating children’s hearing is crucial in pediatric audiology. Unlike adults, children may have difficulty expressing their hearing experiences, requiring audiologists to use creative and child-friendly methods to engage and obtain accurate responses. Creating a comfortable and welcoming environment is essential to build trust and cooperation with young patients during evaluations.
Common Hearing Issues in Children
Hearing issues can significantly impact a child’s development and communication abilities. Some common hearing challenges in children include:
- Congenital Hearing Loss: Present at birth, it can range from mild to profound and may have genetic or environmental causes.
- Acquired Hearing Loss: Caused by infections, injuries, loud noises, or certain medications after birth.
- Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Inflammation in the middle ear due to infections, leading to temporary hearing loss.
- Auditory Processing Disorder (APD): Difficulty processing auditory information despite normal hearing sensitivity.
- Noise-induced hearing Loss (NIHL): Caused by exposure to loud noises, such as loud music or fireworks.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Impaired equalization of ear pressure, leading to recurrent ear infections.
- Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder (ANSD): Rare condition affecting sound signal transmission to the brain.
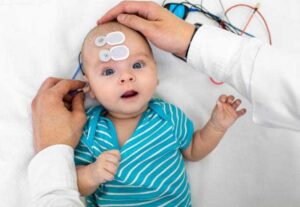
Importance of Early Detection in Hearing
Early detection of hearing issues in children is of paramount importance as it significantly impacts their overall development and future success. Identifying and addressing hearing challenges as early as possible offers several crucial advantages:
1. Language and Communication Development
During the early years of life, children’s brains are highly receptive to language development. Hearing plays a fundamental role in speech and language acquisition. If a child has undetected hearing loss, it can hinder their ability to hear and imitate sounds, leading to delays in language development. Early intervention can help bridge these gaps and provide children with the necessary support to catch up with their peers.
2. Academic Performance
Hearing difficulties can impede a child’s learning in the classroom. Children with untreated hearing loss may struggle to follow instructions, participate in discussions, and comprehend educational material. Consequently, their academic performance may suffer, affecting their overall educational journey. Timely detection and appropriate interventions can ensure that children have access to optimal learning opportunities, setting them on a path to academic success.
3. Social and Emotional Well-being
Communication is vital for building social connections and emotional well-being. Children with untreated hearing issues may experience feelings of isolation, frustration, and low self-esteem, as they might find it challenging to interact and communicate effectively with peers and family members. Early detection and intervention can enhance a child’s social interactions, fostering positive emotional development and building stronger relationships.
4. Preventing Developmental Delays
Early detection of hearing problems allows healthcare professionals to address issues before they cause significant developmental delays. Early intervention services, such as hearing aids or speech therapy, can help minimize the impact of hearing loss on a child’s development, ensuring they reach critical milestones in their cognitive, emotional, and physical growth.
5. Optimizing Treatment Outcomes
The human brain is most plastic and adaptable during early childhood. This neuroplasticity means that early intervention can lead to more effective results in terms of hearing improvement and language development. By identifying and addressing hearing issues promptly, healthcare providers can capitalize on the brain’s natural ability to adapt and promote better outcomes.
The Pediatric Audiology Evaluation Process
The pediatric audiology evaluation process is a comprehensive and child-friendly approach designed to assess a child’s hearing abilities accurately. Each step is carefully tailored to the child’s age and developmental stage, ensuring a comfortable and engaging experience. Here’s an overview of the evaluation process:
- Case History and Parental Interview: Gathering relevant information about the child’s medical and hearing history.
- Behavioral Observation: Observing the child’s responses to sounds for younger children who cannot perform traditional tests.
- Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (VRA): Using animated toys or lights as rewards when the child responds to sounds.
- Play Audiometry: Engaging older children with games that involve responding to sounds.
- Pure-Tone Audiometry: Testing older children’s hearing using headphones and response cues.
- Tympanometry: Assessing middle ear function to detect any issues.
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) and Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR): Objective tests to evaluate inner ear and auditory nerve function.
The results guide audiologists in diagnosing hearing issues and creating personalized treatment plans for each child. Early intervention can significantly improve a child’s hearing abilities and overall quality of life.
Supporting Children and Their Families
When a child is diagnosed with a hearing issue, it impacts not only the child but also their family. The journey of navigating through hearing challenges can be overwhelming, but there are various ways to support both the child and their loved ones during this process:
- Family Counseling and Education – Offer counseling and educational resources to help the child’s family understand the hearing issue and available treatment options. Educate them about communication strategies and assistive technologies to actively participate in the child’s development.
- Parent Support Groups – Connect families with support groups of parents who have experienced similar situations. Sharing experiences and advice within a supportive community can provide comfort and reassurance.
- Early Intervention Programs – Encourage enrollment in early intervention programs focused on language and communication development for children with hearing impairments.
- Collaboration with Schools and Educators – Collaborate with schools and educators to create individualized education plans (IEPs) accommodating the child’s hearing needs in the classroom.
- Speech and Language Therapy – Provide access to speech and language therapy to improve communication skills.
- Assistive Listening Devices – Recommend and provide assistive listening devices, such as hearing aids or FM systems, to enhance the child’s hearing experience.
- Advocacy and Rights – Advocate for the child’s rights to ensure appropriate accommodations and support in various environments.
- Emotional Support – Offer emotional support to the child and their family throughout the journey.
- Celebrating Milestones – Acknowledge the child’s achievements and milestones, boosting their self-esteem and motivation.
- Continuous Monitoring and Follow-up – Ensure regular follow-up evaluations and monitoring of the child’s hearing and development.
Take the First Step to Better Hearing: Try Our Online Hearing Test Today!
Ready to hear better? Experience personalized hearing care at Listen Hear Diagnostics, your leading hearing specialist and audiologist in Westchester. Take our quick and convenient Online Hearing Test to kickstart your journey to improved hearing health!
Our expert team offers comprehensive hearing tests, advanced hearing aids from top brands, and effective tinnitus treatment in Westchester. We understand that hearing loss impacts individuals uniquely, and our goal is to tailor treatments to meet your specific needs.
Don’t miss out on the sounds of life. Contact us today at (914) 902-8845 or visit our office at 161 Central Park Ave, Hartsdale, NY 10530. Let’s work together to enhance your quality of life through better hearing! Listen Hear Diagnostics – Your path to better hearing starts here.